

 Vol. 39 (Number 12) Year 2018. Páge 11
Vol. 39 (Number 12) Year 2018. Páge 11
Alexandra V. GLUSHСHENKO 1; Yekaterina P. KUCHEROVA 2
Received: 01/11/2017 • Approved: 30/11/2017
ABSTRACT: The current research presents the analysis of the integrated agricultural formations’ activity and modern agricultural holdings’ development and functioning tendencies in terms of the global financial crisis. The research authors suggest and prove the methodic of lowering the credit risk for the integrated agricultural formations, which will enable forming and using the ABC-analysis of account-analytical information for modeling the anti-crisis strategy for the agricultural structure’s interaction with buyers groups. The research suggests the pattern of recording the information on an agricultural holding’s profitability of interacting with external buyers by distributing the buyers with the help of the ABC-analysis into segments: A-segment- “highly profitable buyers”, B-segment - “problem buyers” and C-segment - “low-profit buyers” (taking into account the intervals for the segments). The article also suggests an algorithm of functional calculating the commercial expenses by the agricultural holding’s buyers (Activity-based costing) and provides the mechanism of a step-by-step integration of a set of measures on lowering the credit risk into the agricultural holdings’ activity. Such mechanism includes 3 stages: basic, analytical and final. The research authors elaborate a special management and segment accounting registers in order to accumulate the account-analytical information on an agricultural holding’s profitability of interacting with external buyers. And finally, the research authors define the absolute and relative indicators, used management and segment accounting registers, which form the information provision conceptual approach to the strategy of an agricultural holding’s long-term interaction with the buyers. |
RESUMEN: La presente investigación muestra el análisis de la actividad de las formaciones agrícolas integradas y las tendencias de desarrollo y funcionamiento de las explotaciones agrícolas modernas en términos de la crisis financiera mundial. Los autores de la investigación sugieren y prueban la metódica de reducir el riesgo de crédito para las formaciones agrícolas integradas, lo que permitirá formar y utilizar el análisis ABC de información analítica de cuenta para modelar la estrategia anticrisis para la interacción de la estructura agrícola con grupos de compradores. La investigación sugiere el patrón de registrar la información sobre la rentabilidad de una tenencia agrícola interactuando con compradores externos mediante la distribución de los compradores con la ayuda del análisis ABC en segmentos: segmento A, "compradores altamente rentables", segmento B, "problema" compradores "y del segmento C -" compradores con bajos beneficios "(teniendo en cuenta los intervalos para los segmentos). El artículo también sugiere un algoritmo de cálculo funcional de los gastos comerciales de los compradores de la explotación agrícola (costeo basado en actividades) y proporciona el mecanismo de una integración paso a paso de un conjunto de medidas para reducir el riesgo de crédito en las explotaciones agrícolas. actividad. Tal mecanismo incluye 3 etapas: básica, analítica y final. Los autores de la investigación elaboran registros especiales de administración y de contabilidad de segmentos para acumular la información analítica de la cuenta sobre la rentabilidad de una explotación agrícola para interactuar con compradores externos. Y, finalmente, los autores de la investigación definen los indicadores absolutos y relativos, los registros de contabilidad de gestión y de segmentos utilizados, que forman el enfoque conceptual de provisión de información para la estrategia de interacción de largo plazo entre la explotación agrícola y los compradores. |
The global economic system is actively forming and developing. Its borders and existence conditions are constantly changing, which is followed by crises that which damage global economy members’ own economies.
Being global and systemic, the modern finance crisis has helped to define the drawback of the theoretical approaches to elaborating practical overcoming crisis methods, which are applied in terms of managing the integrated agricultural formations. This determines the necessity to improve the global crisis-management system, what will facilitate adequate response to crisis phenomena, based on innovative approaches and application modern account-analytical methods and tools.
“Global crisis management implies coordinated actions, aimed at preventing crisis development, decreasing its tension and eradicating its negative consequences” (Nato Logistics Handbook. Definitions.).
Being the main subjects of financial globalization, integrated agricultural formations face the risks more often than the companies, which operate on national markets, besides these risks are both common for all business spheres and specific, characteristic of international operations only.
On the one hand, the financial and food markets’ globalization gives an opportunity to the integrated agricultural formations to compare and evaluate the investments’ efficiency simultaneously in the framework of the international economy; extend and consolidate the financing potential of diverse economic projects. On the other hand, the world economy’s qualitative changes are of a deep and risky character, which is caused by rapid finance innovations development, what in turn leads to the rapid growth of the system risk and financial risks of the economies’ international activity.
R. Alborov, N. Belov, M. Bychkov, F. Vaskin, A. Larionov, M. Ovsiychuk, L. Perekrestova, M. Pizengolts, T. Rogulenko, L. Khoruzhiy, V. Shirobokov have devoted several research works to studying the account-analytical provision system’s functioning and organization in the agricultural sphere. Several scientists, such as O. Burlakova and N. Gorlova, investigated the issues of organizing the accounting in the integrated economic structures.
G. Afanasiyev, A. Barinov, A. Gradov, V. Davydov, M. Yefimova, I. Larionov, Y. Novoselov, V. Potemkin, V. Romanichev have investigated theoretical and practical issues of crisis management. N. Tom and J. Ruegg-Schturm have paid special attention to managing the changes, which are provoked by the crisis development.
However, the contemporary crisis management studies do not take into account the sectorial peculiarities of the agricultural sphere and specific risks, characteristic of the integrated agricultural formations. In addition to it, there aren’t many studies, devoted to the methods of lowering the integrated agricultural formations credit risk in terms of the global crisis management. In this regard, it is considered that it is essential to elaborate a complex of methodic recommendations on lowering the credit risk for the integrated agricultural formations.
Solving the aforementioned problem demands applying the analysis and synthesis methods, grouping and comparing, modeling, system and complex approaches, which enable us to clarify possible solutions and provide research results’ authenticity.
According to the Agricultural Market Studies Institute, more than 200 agricultural holding were operating in Russia as of January 1, 2014 and provided 20-25% of the production volume in the agricultural sphere. The total square of the farm land, belonging to the agricultural holdings equals to 15 million hectares, 11.3 million hectares of which is arable land. According to the media holding Expert, which has been for more than 10 years forming the rating of the “Largest Sales Volume Companies”, in 2014, 11 companies out of 400 were integrated agricultural holdings (See Table 1) (Largest Sales Volume Companies”, 2015. Reference date: 20.09.2016).
Table 1
Largest Russian Federation Agricultural Holdings by their Sales Volume in 2014
No. |
Name |
Rank |
Sales Volume |
Pre-tax Profit |
Net Gain |
1 |
Miratorg |
150 |
53,683.0 |
9,759.0 |
9,615.0 |
2 |
The Cherkizovo Group |
151 |
52,808.5 |
2,118.7 |
2,051.0 |
3 |
The EFKO Group |
161 |
50,213.0 |
586.0 |
414.0 |
4 |
Ug Rusi |
163 |
50,070.5 |
280.7 |
156.8 |
5 |
Rusagro Group |
221 |
36,489.8 |
3,532.7 |
3,201.8 |
6 |
Ostankinskiy MPK |
296 |
27,240.2 |
1,168.8 |
958.7 |
7 |
Prioskole |
298 |
27,079.5 |
372.1 |
309.8 |
8 |
Solnechnyye Produkty |
318 |
25,167.2 |
441.7 |
336.9 |
9 |
Kosmos Group |
351 |
22,315.5 |
27.6 |
-84.3 |
10 |
Prodimex Holding |
354 |
21,890.1 |
96.7 |
75.6 |
11 |
APK Aston |
379 |
19,468.4 |
555.8 |
495.6 |
Integrated agricultural formations in Volgograd Oblast are an important economic sector of the region, which significantly influence its social and economic development. Over the last years, the agricultural holdings’ sectorial activity has increased. Ten Volgograd Oblast’s agricultural holdings, which possess diverse financial and labor resources, function most successively. They include Vostok CJSC (Nikolayevskiy District), Volzhskiy Udarnik LLC (Chernyshkovskii District), Gelio-Paks-Agro LLC (Novoanninskii District), and Delta-Agro OJSC (Mikhailovskii District) (The largest and most effective agricultural enterprises).
Under the conditions of the world market’s significant volatility, complicated management system, and territorial isolation of the agricultural enterprises that comprise an agricultural formation, the activity and markets’ diversity demands elaborating and implementing a new crisis management strategy in the framework of an overall integrated agricultural formation’s strategy, aimed at the agricultural holding’s sustainable economic development. Besides, the global financial market provokes special risks to the agricultural formations, such as the monetary (operational, translational, and economic), country-specific and credit risk (del credere risk).
The credit risk (del credere risk) is the failure of a buyer to pay or his/ her partial payment or the untimely payment for the goods received, evolved by the buyer’s own unreliability, inability to pay or the seller’s contract rules violation (Lednev, 2010).
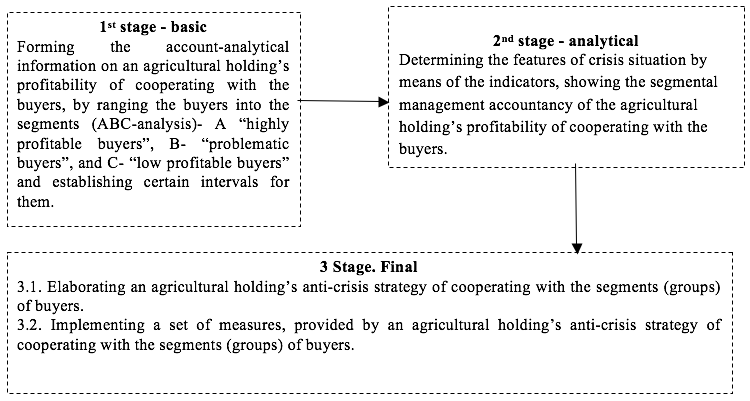
A business’s sustainability and expansion is usually achieved by analyzing the monetary and state risks by the consolidated accounts’ general indicators (gains, losses, debt, profit and etc.). However, achieving these goals lacks paying certain attention to evaluating the agricultural goods buyers’ certain investment into an integrated company’s profit - the del credere risk. Along with it, it is not reasonable for an agricultural holding to develop long-term cooperation with any types of buyers, as their demands character is not homogenous (and their corresponding satisfaction demands) leads to varying efficiency and risk levels. Taking this into account, the current research presents a set of procedures distributed into three stages: 1) the basic stage- forming the account-analytical information on an agricultural holding’s profitability of cooperating with the buyers, by ranging the buyers into the segments (ABC-analysis)- A “highly profitable buyers”, B- “problematic buyers”, and C- “low profitable buyers” and establishing certain intervals for them; the analytical stage - determining the features of crisis situation by means of the indicators, showing the segmental management accountancy of the agricultural holding’s profitability of cooperating with the buyers; the final stage- elaborating an agricultural holding’s anti-crisis strategy of cooperating with the segments (groups) of buyers and implementing a set of measures, provided by an agricultural holding’s anti-crisis strategy of cooperating with the segments (groups) of buyers.
The article presents an algorithm of measures for the agricultural holdings to implement in order to decrease the credit risk (Figure 1).
Fig. 1
The algorithm of measures for the agricultural holdings to implement in order to decrease the credit risk
We consider it reasonable to for an agricultural holding to establish the Methodology and Segmental Accountancy Standardization department in order to form the account-analytical information on an agricultural holding’s profitability of cooperating with the buyers. This department’s functions will include: developing the segmental accountancy methodology and inter-holding standardization; launching and segmental accounting and agricultural formation’s member-companies; an integrated agricultural formation’s information and program support, elaboration and implementation of an anti-crisis strategy, which will give the opportunity to decrease management costs, accumulate, distribute the agricultural holding’s resources in a better and more reasonable way by the holding’s activity segments and minimize the risks.
At the 1st stage, which deals with forming the account-analytical information on an agricultural holding’s profitability of cooperating with the external buyers, we suggest limiting these buyers by the “cooperation profitability” criterion to a certain number of segments (groups), what will help getting discrete and relevant accounting data.
Cooperation profitability is the quantitative indicator, characterizing the agricultural holding’s efficiency of cooperating with the buyer and expedience of maintaining long-term cooperation with him.
We have used the ABC-analysis for distributing these buyers by the level of their investment into the consolidated profit. ABC-analysis is a universal method, applied for rationalizing a company’s various activity spheres, by distributing its resources (goods in stock, suppliers and buyers and etc.) through the Pareto principle into 3 (more rarely 4-5) groups: A - the most valuable (20% of the resources provide 80% of the result), B - intermediate (average return) and C - the least valuable (low profitable, when 50% of the resource provide 5% of the result).
As a result of analyzing of the substantive nature and scope of the ABC - analysis, we suggest the methodology of forming segmental management accountancy on the profitability of agricultural holdings cooperation with buyers, including the following stages:
I. Calculation of "cooperation profitability" indicator for each agricultural product and service buyer.
II. Establishing limits for the segments A – “highly profitable buyers”, B – “problem buyers”, and C – “low-profit buyers” on the basis of the “cooperation profitability” indicator.
III. Ranking the buyers by segments, depending on the “cooperation profitability” indicator level, in accordance with the calculated interval limits.
IV. Formation of segmental accountancy on the agricultural holding’s cooperation with the buyers’ profitability.
To calculate the “cooperation profitability” relative indicator, which is the basis of segmenting the buyers, an agricultural holding’s cooperation with the buyers prime cost is determined, as while providing the services different in content and value trade costs are formed.
The complexity of generating information about the trade costs in the accounting agricultural holdings’ information system is the weight of non-production costs to sales costs, which are indirect, in relation to goods being produced and are determined to a greater degree not by the volume of production but by the kinds of activities (processes and operations), consuming corresponding resources. Thus, it a more appropriate method of distributing the costs from the accounting objects - elements and cost items, to the calculation objects - agricultural production buyers. This is the Activity-based costing method. It is the functional calculation based, unlike the conventional methodic, on the cause and effect link between resources and process results, what allows making a large part of the overhead costs direct.
Analyzing the complex of services, provided by the agricultural holding while selling its production, helps determining the costs, associated with cooperation with the buyers, identifying these costs by the activity kinds, and grouping them by the ways of including in the prime cost into direct and indirect (Figure 2).
Fig. 2
The two-stage process of distributing labor costs in the functional calculation system
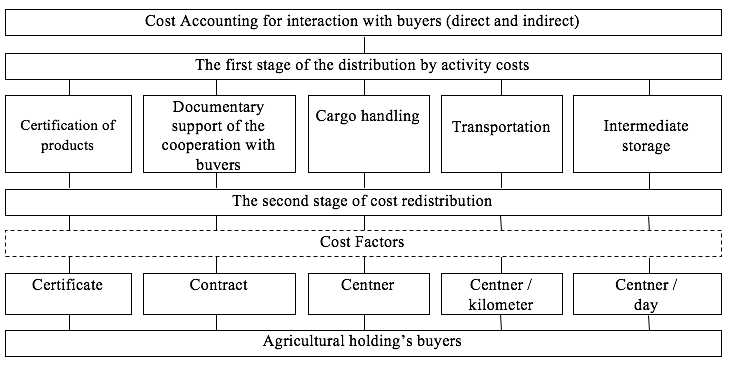
The result of taking consequent actions on identifying, grouping and distribution the costs on the services (provided to buyers) is making up the step-by-step ABC-calculation. When distributing the indirect costs, we have applied the functional system of distributing the costs (Activity based costing), which allows getting more precise information about the costs for each group of the agricultural holding’s external buyers.
In order to distribute the costs by the activities, we have elaborated the “Cost factor account rate” and the “Prime cost of cooperating with the buyer”, on the basis of which we can make up the suggested “The agricultural holding’s cooperation with its external buyers profitability report” (Table 2). The report comprises 2 groups of indicators: absolute and relative.
“In order to make the ABC - segmenting of buyers according to the “cooperation profitability”, criterion we consider it appropriate to use flexible intervals for each segment, allowing to reduce the quantitative trait and improve the qualitative characteristics of the indicator. The boundaries of the segments are set as a percentage of its maximum achieved value of the indicator “profitability of interaction”, calculated according to all buyers of agricultural holding” (Glushchenko and Kucherova, 2015).
Establishing the limits for the intervals for the segments is based on the professional judgment of the agricultural holding’s accountant. For buyers of agricultural holding segmentation criteria proposed offer to install the following intervals segments:
A – “highly profitable buyers”. This segment form buyers with the level of the indicator, forms the basis of segmentation for more than 80% of its maximum value achieved profitability interaction, calculated from all buyers of agricultural holding.
B – “problem buyers”. Buyers falling within this segment should be calculated index value in the range (50%; 80%) of the maximum level of profitability achieved by the interaction of values calculated from all buyers of agricultural holding.
C – “low-profit buyers”. Buyers are attributable to this segment must have a level index of less than 50% of its maximum achieved value of the indicator “profitability of interaction”, calculated according to all buyers of agricultural holding.
Table 2
The agricultural holding’s cooperation with its external buyers profitability report
Name of purchaser: FAROSS LLC |
||||
Name of products sold: winter wheat |
||||
No. |
Indicator name |
Prior period |
Reporting period |
|
01 |
Production cost, RUB/c. |
85 |
94 |
|
Terms of selling |
|
|||
02 |
Prepayment percentage, % |
50 |
30 |
|
03 |
Granted discounts % |
5 |
5 |
|
04 |
The sales volume, c. |
1,400 |
1,000 |
|
05 |
Price, RUB / c. |
750 |
850 |
|
Trading activities |
|
|||
06 |
Certification of products, RUB |
16,200 |
23,800 |
|
07 |
Documentary support to the cooperation with the buyers, RUB |
1,800 |
4,194 |
|
08 |
Interim storage, RUB |
х |
100,000 |
|
09 |
Cargo operations, RUB |
х |
11,000 |
|
10 |
Transportation, RUB |
850,000 |
400,000 |
|
11 |
TOTAL |
868,000 |
538,994 |
|
|
||||
12 |
Sales Profit (04*05), RUB |
1,050 000 |
850,000 |
|
13 |
Granting discounts, RUB |
52,500 |
42,500 |
|
14 |
Revenue excluding discounts (12-13), RUB |
997,500 |
807,500 |
|
15 |
Gross profit, RUB (14-(01*04)) |
878,500 |
713,500 |
|
16 |
Income per buyer, RUB (15-11) |
10,500 |
174,506 |
|
INTERACTION PROFITABILITY, % (16/14*100%) |
0.01 |
0.22 |
||
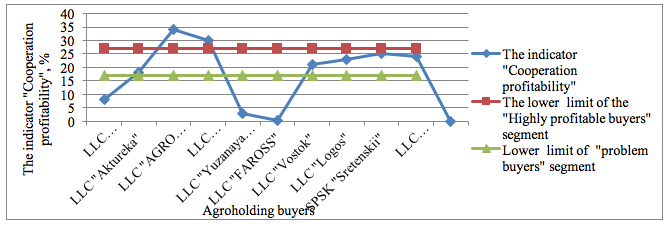
As a result, the calculation of the indicator “cooperation profitability” for all buyers of agricultural holdings, set its maximum value equal to 34%. In accordance with the proposed intervals segments each border with ABC - analysis will have the following meanings:
- Segment A – “highly profitable buyers” form a relevant indicator of “return on engagement” more than 27.2% (34 * 0.8);
- Segment B - "problem buyers” form buyers value of the indicator “interaction margin”, which is in the range of 17% to 27.2%;
- Segment C – “low-profit buyers” comprise a position indicator value “return on engagement” less than 17%.
Furthermore, the buyers are ranked by segments, depending on the “profitability level” in accordance with the interval limits. Figure 3 presents the segmentation into 3 segments.
Figure 3
ABC- segmentation of buyers by the “cooperation profitability” indicator
Based on the data generated registers, the segmental report on the profitability of agricultural holding’s cooperation with customers is compiled. In order to make informed management decisions it is important to determine the optimal number of indicators, is usually sufficient allocation from 5 to 10 indicators of the efficiency of interaction with customers. In tabular form the proposed segmental report on the profitability of agricultural holding’s cooperation with customers (Table 6) allocated two groups of indicators: the absolute and relative, most fully characterize the effectiveness of the relationship with customers. The proposed form has its focus, which is consistent with the principle of targeted reporting.
On the next stage a manager is to determine the crisis situation features, basing on the indicators of the segmental accountancy of on the agricultural holding’s cooperation with the buyers profitability. Maximum control action should be directed to the segment C – “low-profit customers”, formed of Roshhinskoye LLC, Yuzhnaya Kormovaya Kompaniya LLC, and FAROSS LLC. These agricultural production buyers show the lowest level of cooperation profitability and the highest credit risk.
On the final stage, basing on the results of the analysis of the segmental accountancy, we model an anti-crisis strategy of an agricultural formation’s cooperation with the groups of buyers, which is a system of long-term conceptual trajectories of an agricultural holding’s interrelations with each segment (group), which includes 3 blocks: conceptual, strategic, and program. The strategy’s structure is shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4
The structure of the agricultural holding’s cooperation with buyers
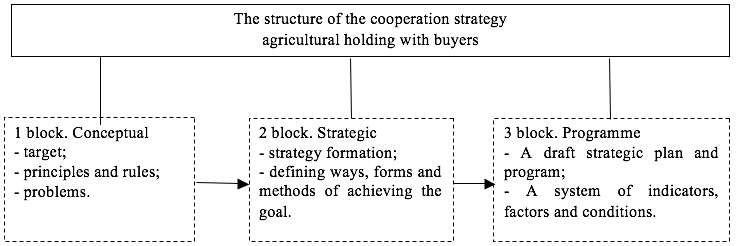
The segment “highly profitable buyers” is the most valuable one; the strategy of interaction with this group is to work with preferred terms of cooperation (increase in the percentage of discounts, the use of incentive programs, etc.), in order to preserve this segment.
For further interaction with the segment “problem buyers” it is necessary to analyze information on this group to identify additional opportunities in order to improve the profitability of interacting with them. Perhaps, there are additional opportunities in this group to improve profitability by providing them with more favorable terms. In the work with the segment “low-profit customers” the indicators for this group should be analyzed, as almost half of these buyers are unprofitable for the agricultural holding. However, these drawbacks may turn into advantages in negotiations to amend the terms of cooperation with them.
The implementation of the elaborated methodology on lowering the credit risk will help the integrated agricultural formations to form the account-analytical information on an agricultural holding’s profitability of cooperating with the external buyers, basing on the ABC-analysis results, which can be further used to develop an anti-crisis strategy for the agricultural formation’s cooperation with groups of buyers.
Glushсhenko A., Zemlyanskaya Ye., 2015 Methodic on management accountancy on an agricultural holding’s cooperation with the buyers profitability/ Volgograd State University Vestnik. Series 3. Economics. Ecology, No. 04 (33): C. 255-267.
Lednev, M., 2010. Managing the Risks of a Factoring Company’s Activity/ “Financial risks management”, No. 2: P. 78-90.
Russia’s largest Companies Rating by their Sales Volume. The Expert Media Holding. http://expert.ru/ratings/rejting-krupnejshih-kompanij-rossii-2014-po-ob_emu-realizatsii-produktsii (Accessed: September 20, 2016).
The Largest and Most Efficient Agricultural Enterprises Rating. http://agroobzor.ru/info/ratingagro300.html.
Nato Logistics Handbook. Definitions. http://www.nato.int/docu/logi-en/1997/defini.htm.
1. Volgograd State University, Volgograd, Russia. e-mail: ag@volsu.ru
2. Volgograd State University, Volgograd, Russia. e-mail: audit@volsu.ru