

Vol. 38 (Nº 34) Año 2017. Pág. 34
Yuliya Evgenievna KLISHINA 1; Irina Ivanovna GLOTOVA 2; Olga Nikolaevna UGLITSKIKH 3; Elena Petrovna TOMILINA 4; Irina Michailovna PODKOLZINA 5
Recibido: 06/06/2017 • Aprobado: 30/06/2017
ABSTRACT: This article analyzes the problem of improving tools for the formation and implementation of the financial policy of non-profit organizations, when, in the context of emerging crisis trends, there is a need for periodic changes in certain provisions of financial policy at the macro and micro levels. Despite a significant number of publications on the development of theory and methodology for the formation of the organization's financial policy, there remains a need to study the problems of developing the financial policy of non-profit organizations. In this connection, the authors substantiate the provisions for improving the elements of the financial policy of non-profit organizations in the unstable macroeconomic environment and make practical recommendations for managing the financial risks of non-profit organizations. In particular, an algorithm for managing the financial risks of non-profit organizations has been formed, which makes it possible to raise the level of their financial stability through the formation of financial policy that takes into account the specifics of the activity of these organizations; to develop a set of financial planning procedures that help diversify the sources of funds and the directions of their use with a view to obtaining additional revenues in the implementation of statutory goals; to make adjustments to the system of financial and organizational relations to support publicly significant projects at the federal and regional levels. |
RESUMEN: Este artículo analiza el problema de la mejora de las herramientas para la formación y aplicación de la política financiera de las organizaciones sin fines de lucro cuando, en el contexto de las tendencias de las crisis emergentes, se necesitan cambios periódicos en ciertas disposiciones de la política financiera macro y Micro niveles. A pesar de un número significativo de publicaciones sobre el desarrollo de la teoría y la metodología para la formación de la política financiera de la organización, sigue siendo necesario estudiar los problemas de desarrollo de la política financiera de las organizaciones sin fines de lucro. A este respecto, los autores fundamentan las disposiciones para mejorar los elementos de la política financiera de las organizaciones sin fines de lucro en el entorno macroeconómico inestable y formulan recomendaciones prácticas para la gestión de los riesgos financieros de las organizaciones sin fines de lucro. En particular, se ha formado un algoritmo para gestionar los riesgos financieros de las organizaciones sin fines de lucro, que permite elevar el nivel de su estabilidad financiera mediante la formulación de una política financiera que tenga en cuenta los aspectos específicos de la actividad de estas organizaciones; Desarrollar un conjunto de procedimientos de planificación financiera que ayuden a diversificar las fuentes de fondos y las direcciones de su uso con el fin de obtener ingresos adicionales en la implementación de los objetivos estatutarios; Para hacer ajustes en el sistema de relaciones financieras y de organización para apoyar proyectos de importancia pública a nivel federal y regional. |
The need for the functioning of such an organizational and legal form as a non-profit organization can be explained by the fact that the state's provision of public goods to the population is associated with the consumption of national income, and therefore its possibilities in this area are limited. But if the state had the opportunity to satisfy the needs of all citizens for public goods, this would require the creation of a multi-level, complexly managed system of their distribution, and it would be unlikely to achieve an uninterrupted and efficient functioning of such a system in the economy of any state (Shubina and Sukhorukikh, 2005).
In this connection, it is advisable to transfer the solution of the problem of ensuring citizens' access to the entire range of public goods directly from the state level to the level of participants in civil turnover in the form of non-profit organizations, one of the main components of civil society (Tatuev and Bahturazova, 2014; Gutnik et al., 2016).
In international practice, non-profit organizations are created to solve the tasks, with which government bodies and local self-government bodies are dealing on a daily basis, such as to care for low-income socially disadvantaged citizens, to promote moral and aesthetic education for children and adolescents, to raise the level of education for the population, to preserve and develop cultural heritage in society, to effectively protect the rights and freedoms guaranteed by the Constitution of the Russian Federation, and much more that cannot be provided by for-profit organizations (Grischenko, 2012). In a number of ways, non-profit organizations operate more successfully and economically than state institutions, which is confirmed by studies carried out in many countries - the USA, Germany, France, Sweden, etc. (Mertl, 2016).
For the Russian reality, when the state is able to finance public goods only on a very limited scale, the development of the non-profit sector can make a significant contribution to enhancing stability in society.
One of the important conditions for the functioning of non-profit organizations in a market economy is their financial activity (Volgunina, 2011). The effective implementation of the concept of financial management of a non-profit organization requires the development of the main areas of its financial policy. Establishing the goals, objectives and ways of functioning of the economic entity, financial policy should determine the prospects for the development of a non-profit organization, priority areas of its activities as well as be developed in conditions of the risks and cyclicality of economic processes (Sebestova and Palova, 2015).
The formation of financial policy on the appropriate theoretical and methodological basis contributes to the balance between the organization and the environment and to the sustainable operation of the economic entity - a for-profit or non-profit organization. The financial policy of economic entities is interrelated and interdependent on the financial policy of the state, whose priority objective is the smoothing of economic cycles, the improvement and restructuring of the economy, the development and effective functioning of economic sectors, the qualitative improvement of the living standards of the population, an increase in the efficiency of the use of financial resources as well as the provision of financial-economic and social stability in the country on the basis of economic growth.
The theoretical and methodological foundations of financial policy are directly related to the formation of the theory of finance, the founders of which are Diomede Caraffa, Jean Bodin, Francois Quesnay, Adam Smith, David Ricardo, Jean Sismondi and others. The development of a market economy, which is characterized by the relative freedom of choice of the subject of activity and the ways of attracting and using financial resources, determines the organization’s financial policy as an independent field of scientific research.
The theoretical-methodological and organizational-methodological aspects of the organization’s financial policy and its development were presented in the works of N.I. Berzon, I.A. Blank, A.Z. Bobyleva, Z. Bodie, R. Brealey, I.V. Ivashkovskaya, V.V. Kovalev, N.P. Lyubushin, R. Merton, M. Miller, V.I. Petrova, A. Raviv, S. Ross, M. Haris, A.D. Sheremet and others. Financial accounting was explored by Yu.A. Babayev, M.R. Matthews, B. Needles, S.A. Nikolayeva, the issues of audit of the financial policy of organizations – by V.V. Burtsev, V.G. Kogdenko, L.R. Kurmanova, O.N. Likhacheva, M.V. Melnik, L.V. Perekryostova, T.N. Pestryakova, E.A. Prikhodko, T.P. Satsuk, V.A. Slepov, V.A. Shcherbakov and others.
The questions of research of the organization’s financial policy are based, as a rule, on the provisions of the financial policy of the state and regions set out, particularly, in the works of A.G. Gryaznova, L.A. Drobozina, G.G. Korobova, L.N. Pavlova, Т.F. Romanova and other researchers.
At the same time, there remains a need to study the problems of developing the financial policy of non-profit organizations.
The formation of the organization’s financial policy is based on a set of principles: objectivity, sustainability, planning, systematicity (unity), economic expediency, scientific validity.
The principles of objectivity and sustainability determine the need to take into account the objective processes occurring in the socio-economic system of the business entity as well as their predictable change in the formation of the organization’s financial policy. The provisions of financial policy should be mandatory for implementation and be reflected in a special planning document for a certain period. This contributes to the implementation of the principles of commitment, planning and urgency. Continuity in financial policy means that its purpose, tasks, conceptual directions and approaches to formation do not depend on the change in the administrative and managerial staff of the organization. According to the principle of systematicity, the organization’s financial policy is a set of interrelated elements. The principle of economic expediency implies that the profitability of the implementation of decisions provided by the organization’s financial policy should be ensured. In accordance with the principle of scientific validity, the basis for the formation of the organization's financial policy should be a scientifically grounded concept that contains the rationale for the objectives and tasks of the financial policy of the business entity, the characteristics of the financial and economic processes for which financial policy is formed, the choice of the way of process modeling, the substantiation of the criteria and methods of management of the named processes, their elements as well as the tools of the formation of financial and economic decisions (Makarov, 2008).
In the context of the unstable macroeconomic situation, there is an ambiguity that arises in the composition and understanding of the types of the organization’s financial policy (Voynova, 2015). The structure of definitions of the types of the organization’s financial policy is not uniform. It reflects either the purpose of the corresponding type of financial policy, managerial decisions and the mechanism for their implementation, or the processes of formulating decisions as well as a combination of these characteristics (Borisova, 2014). Certain types of the organization’s financial policy, in particular, in the field of management of fixed and working capital, accounts payable as well as the formation and distribution of profits correspond to the elements of the financial and economic processes of the organization's activities, which include assets, financing sources, incomes and expenses, financial results, individual economic operations and their totality.
To systemize the types of the organization’s financial policy and justify the problems associated with their formation, A.S. Makarov carried out an analysis of the structure of financial and economic processes that determine the composition and interrelation of their elements. In addition, he provided a rationale for financial and economic processes and their elements, as the objects of the organization's financial policy. With regard to non-profit organizations, we consider it expedient to single out the following composition of the objects of the organization's financial policy (see Figure 1).
Classification of the types and objects of financial policy provides an opportunity to specify its types, purposes and tasks of development. The movement of financial resources and the formation of incomes, expenses, profits (losses) is accompanied by operations for the implementation of entrepreneurial and other income-generating activities by the non-profit organization. A well-known non-profit organization can carry out these activities only because it serves the achievement of purposes for which it was created and meets the stated goals, provided that such activities are specified in its constituent documents. At the same time, the obligation of non-profit organizations to keep records of incomes and expenses on entrepreneurial and other income-generating activities is legislatively fixed (On non-profit organizations: the federal law, 1996).
Figure 1. Objects of the financial policy of non-profit organizations
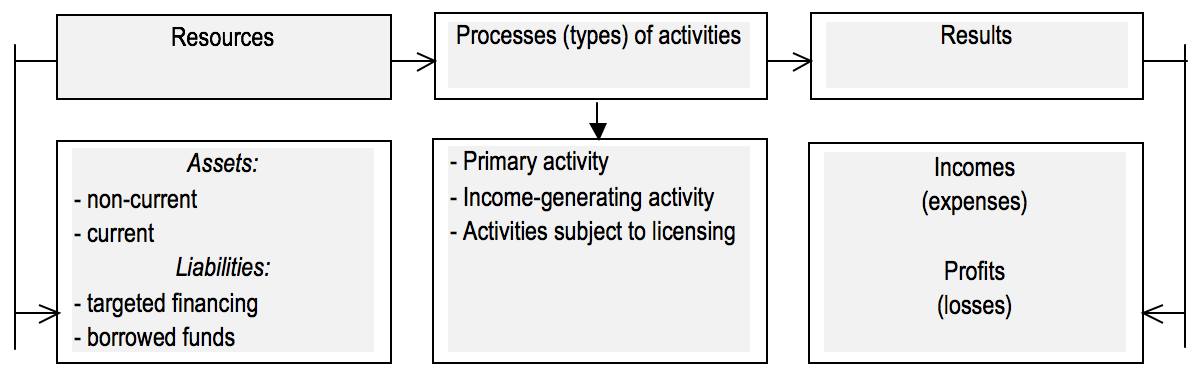
In domestic and foreign theory and practice there is no concept of "the financial policy of the non-profit organization" due to the fact that the activities of these organizations are significantly regulated and the opportunity for independent decision-making is as limited as possible. The main objective of financial activities in the for-profit organization is to accumulate, distribute and use financial resources (Svyaschuk, 2013). The leadership of the non-profit organization faces a slightly different task: it must clearly define the source of the financial and economic activities of the non-profit organization.
In view of the foregoing, we consider it expedient to consider the financial policy of the non-profit organization as a set of measures on the targeted formation, distribution and use of the organization’s financial resources necessary to achieve its statutory goals. The specifics of development of the financial policy of non-profit organizations and its content are determined by the principles of functioning of their finances, organizational and legal form and type of activity as well as (following from the last two factors) the possibility to accumulate and control income from the provision of paid services and the implementation of entrepreneurial and other income-generating activities. The finances of non-profit organizations are characterized by a number of characteristic features of their formation that affect the construction of the financial policy of the non-profit organization and determine its specifics in comparison with the financial policy of the for-profit organization:
- a combination of non-profit goals of the organization's activities with the paid forms of core business and self-employment;
- in contrast to the for-profit organization whose activities are aimed at achieving the main goal of its functioning – profit maximization, and whose financial policy is oriented towards incomes, the policy of the non-profit organization, based on its purpose, is focused on the expenses of the non-profit organization that allow producing public goods or achieving them;
- the limited composition of financing sources and the amount of fund raising for non-profit organizations of certain organizational and legal forms (for example, the maximum annual amount of the individual's donations to the political party is legislated, and the number of legal entities that have such a right is limited);
- significant dependence of the financial and economic activities of the non-profit organization on external financing sources (funds of founders, owners, participants of the organization, charitable and sponsor contributions, subsidies from budgets of all levels and extra-budgetary funds, etc.), and in some organizational and legal forms (for example, public institution) – on the goals and objectives of the financial policy of the organization’s owner;
- a limited nature in carrying out investment policy, since targeted investments by non-profit organizations in most organizational and legal forms, with the exception of consumer cooperatives and non-state pension funds, as well as non-profit organizations that have received the right to create a target capital, are not considered investments;
- the legislative definition of the possibility of carrying out entrepreneurial activities, a list of its types for each organizational and legal form as well as the possibility of using the income received (Appalonova et al., 2015).
The main object of the financial policy of non-profit organizations is financial relations related to the formation of financial resources, their distribution and use for the implementation of the organization’s statutory goals.
In the unstable macroeconomic environment, the priority objectives of the financial policy of non-profit organizations are to find ways to attract additional financial resources for the development and expansion of the organization's activities as well as to ensure the efficient use of accumulated funds for the purposes stipulated by the organization’s constituent documents (Trukhachev et al., 2014; Bokareva et al., 2014). From this perspective, efficiency is understood as the rational and effective use of financial resources available at the disposal of the organization, where increased attention is paid to the quality of goods and services provided by the organization.
In accordance with the stated objectives of the financial policy of non-profit organizations, its main tasks (with the exception of public institutions) include:
- the active use of program-targeted methods in the planning of financial and economic activities of the non-profit organization that assumes its focus on certain final results in accordance with the statutory goals of the business entity;
- the use of mechanisms for attracting private capital of national and foreign investors for the purposes of functioning of the non-profit organization;
- the protection of property rights and interests of the non-profit organization by using various financial instruments;
- the optimization of taxation of the non-profit organization, including the application of tax incentives and other mechanisms to reduce the tax burden in the current tax legislation;
- an increase in the efficiency of using own financial resources, including those obtained from entrepreneurial activities of the non-profit organization. At the same time, such activities should not be carried out to the detriment of the organization’s basic statutory activity or lead to its deterioration;
- the minimization of risks in the process of the organization's activities through the creation of financial reserves;
- the adoption of the most effective decisions in the field of using temporarily free funds, including taking into account the financial risk from the proposed investments.
The organization’s financial activity in all forms of its manifestation is associated with a multitude of financial risks, whose level of impact on the results of this activity and the degree of financial security significantly increase in the unstable macroeconomic environment. Risks accompanying the economic activity of non-profit organizations and generating financial threats form a separate group of financial risks that play a more significant role in the overall risk portfolio of the organization. A significant increase in the impact of financial risks of non-profit organizations on the results of economic activities is caused by the volatility of the external environment – the economic situation in the country, the emergence of innovative financial instruments, the expansion of the sphere of financial relations; the volatility of the financial market and a number of other equally significant factors (Malamut and Blach, 2008).
As a result, the identification, assessment and tracking of the level of financial risks is considered one of the most important tasks in the current practice of financial managers of non-profit organizations.
The financial provision of sustainable development of non-profit organizations in the transition period is a more difficult practical task requiring special methodological justification, because general market risks are imposed by specific transitional risks that need to be taken into account in order to minimize probable losses (Antonova, 2002).
When analyzing the risks of non-profit organizations, one should predetermine those factors and circumstances that can guarantee the sustainable functioning of organizational structures.
The financial stability of non-profit organizations is determined by two groups of factors – external and internal.
External factors include risks determined by the lack of, or decline in, demand for offers delivered by the non-profit organization, the risk of force majeure events – in case of a sharp change in the economic situation in the country, the change in the tax system, bank failures, the change in the payment system and the principles of legal regulation of the work of non-profit organizations.
Internal factors include risks associated with the problems of financing of the work of non-profit organizations and the development of their material and technical base.
If it is impossible for the non-profit organization to carry out its statutory tasks, it can be liquidated by a court decision. Errors in financial planning entail the organization’s inability to fulfill its obligations and can lead to the loss of its liquidity and solvency.
The lack of financial resources entails additional costs associated with the payment of interest on bank loans and, therefore, generates credit risk. The inaccessibility of a progressive material and technical base reduces the degree of sponsors’ trust and limits the ability to perform statutory tasks. Incompetent management leads to losses both in the formation of financial resources and in their use (Zamula and Kuzmicheva, 2014).
Russian and international economists determined three main groups of risks for non-profit organizations: liquidity risk, insolvency risk, and credit risk (Vazhel, 2013; Pavlova and Shopenko, 2004).
In view of the fact that financial risks can be interpreted as the probability of financial losses in the course of carrying out economic activities by the business entity, the financial risks of non-profit organizations are the probability of shortage of financial resources for the implementation of statutory goals as well as financial losses in the process of their financial and economic activities.
In the assessment of financial risks, the organization’s accounting statements are used as initial information: the balance sheet report that records the organization’s financial and property position as of the reporting date; the profit and loss statement that presents the results of financial and economic activities for the reporting period. The main financial risks assessed by organizations are grouped into three groups:
- risks of the loss of solvency;
- risks of the loss of financial stability and independence;
- risks of the structure of assets and liabilities (Lantukh and Kuzmicheva, 2015).
To assess the financial risks of non-profit organizations, special methods and procedures are important, primarily at the microeconomic level, since the non-profit organization can take into account external risks only through asset insurance procedures and overcome losses associated with them only when diversifying its activities.
Given that each group of risks leads to certain losses (Lrn) with certain probability (P(Ar)) and involves costs for overcoming the consequences of the risks (Crn), a generalized formula for estimating the losses of the non-profit organization determined by financial risks can be presented in the following form:
Z = Р(Аr) (Lrn + Crn), (1)
where Z is the losses of the non-profit organization as a result of risk situations;
P(Ar) is the probability of occurrence of a risk situation Ar;
Lrn is the losses as a result of risk events;
Crn is the costs associated with overcoming the consequences of risk events.
The activities of non-profit organizations are characterized by a high level of risk, primarily due to their high dependence on external sources of funding.
The analysis of economists' views on the problems of risks shows that in the context of a stable economy a statistical method of their assessment is most acceptable provided that there is sufficient information on the financial results and costs of the organization. The difficulty is only that the existing statistical base should be representative.
In the context of macroeconomic instability, the use of an expert method of risk assessment is most preferable, since it allows the level of risk to be assessed both for individual activities and projects, and for the entire economic activity of the organization as a whole (Grischenko, 2013).
The financial risk management system can be built into the financial management system or implemented on the basis of a special agreement with a financial and credit institution. To create a financial risk management system, additional costs will be required, while activities to collect information on the factors that affect the financial stability of non-profit organizations and to analyze their specifics may be ineffective, given the sufficient complexity of financial risk management for non-profit organizations (see Figure 2).
In the event of a significant decrease in the effectiveness of this activity, non-profit organizations can exercise their right to unite in associations and unions.
In general, the creation of an effective financial risk management system is important for all non-profit organizations, since such a system opens up opportunities to reduce their aggregate losses, improve their financial status as well as concentrate financial resources on priority development directions.
It is advisable to entrust the necessary information and statistical base to regional associations of non-profit organizations (based on shared cost financing). Another option may be the creation of a specialized firm, whose services could be provided to non-profit organizations on a commercial basis. The third option is the creation of a public (municipal) enterprise to provide non-profit organizations with information services on a gratuitous or commercial basis.
Figure 2. Financial risk management algorithm of non-profit organizations

In the context of the unstable macroeconomic situation, the activities of non-profit organizations are accompanied by various financial risks. In order for non-profit organizations to be able to assess these risks, it becomes necessary to develop special methods and procedures, primarily at the level of economic entities, since the non-profit organization can take into account external risks only through asset insurance procedures and overcome losses associated with them only when diversifying its activities.
It is possible to increase the financial stability of non-profit organizations through 1) the formation of financial policy that takes into account the specifics of activities of these organizations; 2) the development of a set of financial planning procedures that allow diversifying financial resources and directions of their use with a view to obtaining additional revenues when implementing statutory goals; 3) the improvement of the system of financial and organizational relations to support socially significant projects at the federal and regional levels.
Thus, any developing non-profit organization, having well-defined strategic goals, is forced to solve the issue of the formation of financial policy focused on the ability of the non-profit organization to function effectively in the unstable macroeconomic environment in accordance with its statutory goals. At the same time, it is necessary to take into account the following features of the activities of non-profit organizations:
1. External financing; the targeted nature of spending on the basis of approved estimates; the costly characteristic and unprofitability of the activity.
2. Openness of finances, public control, lack of commercial secrets in the activities of the non-profit organization; accountability to the source of financing.
3. Realization of public interests, conduct of activities, provided solely by constituent documents.
Therefore, it should be noted that the market economy sets the task to manage the finance of not only for-profit organizations, but also of non-profit structures that, being integrated into the dynamically developing economic system, are forced to formulate and implement their own financial policy aimed at neutralizing financial risks.
Antonova, I.N. (2002). Financial policy of the Russian Trade Union of Railway Workers and Transport Builders in modern conditions. Non-Profit Organizations in Russia, 3, 23-29.
Appalonova, N., Bazarov, R., Syurkova, S. & Faizrakhmanova, E. (2015). Evaluation of non-profit's approaches towards financial resources optimization: The case of Russia. WMSCI - 19th World Multi-Conference on Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics, Proceedings 1, pp. 27-32
Bokareva, E.V., Chernikova, L.I., Egorova, E.N. & Egorova, S.K. (2014). Functioning and development of target capitals of non-profit organizations. Asian Social Science, 10(23), 223-230.
Borisova, O.V. (2014). Formation of the price policy of non-profit organizations. Non-Profit Organizations in Russia, 6, 45-52.
Grischenko, Yu.I. (2012). Stages of the formation of non-profit organizations in Russia Non-Profit Organizations in Russia, 5, 41-46.
Grischenko, Yu.I. (2013). Financial condition of the non-profit organization. Non-Profit Organizations in Russia, 2, 49-57.
Gutnik, L., Yamey, G., Riviello, R., Meara, J.G., Dare, A.J. & Shrime, M.G. (2016). Financial contributions to global surgery: an analysis of 160 international charitable organizations. SpringerPlus, 5(1), 1558.
Lantukh, A.V. & Kuzmicheva, I.A. (2015). Liquidity risk of commercial banks of the Russian Federation. International Journal of Applied and Fundamental Research, 3(1), 63-67.
Makarov, A.S. (2008). Financial policy of the organization: methods, criteria, formation and realization tools. Finance and Credit, 10(298), 54-60.
Malamut, M.E. & Blach, T.J. (2008). ABA Code Revision Raises Concerns for Democracy and Parliamentary Law in Nonprofits. National Parliamentarian, 1, 1-20.
Mertl, J. (2016). Not being understood well: Some difficulties with non-profit sector utilization in Czech Republic. Social Sciences, 11(1), 14-19.
On non-profit organizations: the federal law of January 12. (1996). No 7-FZ. Collection of Legislation of the Russian Federation. No. 3, art. 145.
Pavlova, E.Yu. & Shopenko, V.D. (2004). Financial risks of non-profit organizations (issues of risk assessment and management). Problems of Modern Economics, 1-2 (9-10), 32-38.
Sebestova, J. & Palova, Z. (2015). Sustainability of financial portfolio of non-profit organisations in the Czech Republic. Proceedings of the 26th International Business Information Management Association Conference - Innovation Management and Sustainable Economic Competitive Advantage: From Regional Development to Global Growth, IBIMA, pp. 395-408.
Shubina, T.V. & Sukhorukikh, L.N. (2005). Features of financial planning in non-profit organizations. Financial Management, 2, 45-48.
Svyaschuk, V.A. (2013). Financial strategy of commercial banks: the theoretical foundations. Modern Scientific Researches and Innovations, 3(23), 12-14.
Tatuev, A.A. & Bahturazova, T.V. (2014). Personal savings: controversial role in extended reproduction. Life Science Journal, 11(12), 375-379.
Trukhachev, V.I., Mazloev, V.Z., Sklyarov, I.Y. & Sklyarova, Y.M. (2014). Analysis of the market for agricultural products in South Russia. American-Eurasian Journal of Sustainable Agriculture, 8(6), 52-59.
Vazhel, E.S. (2013). The basis of financial management. Kyiv: Molodezh.
Volgunina, V.N. (2011). Features of the analysis of the non-profit organization’s financial state. Non-Profit Organizations in Russia, 3, 52-60.
Voynova, E.L. (2015). The main directions of the financial policy of Russia in the conditions of economic recession. Modern Scientific Researches and Innovations, 4(48), 5-7.
Zamula, E.V. & Kuzmicheva, I.A. (2014). Tax risks of enterprise and ways of their minimization. International Journal of Applied and Fundamental Research, 8(3), 118-122.
1. Stavropol State Agrarian University, Stavropol, Russian Federation.
2. Stavropol State Agrarian University, Stavropol, Russian Federation.
3. Stavropol State Agrarian University, Stavropol, Russian Federation.
4. Stavropol State Agrarian University, Stavropol, Russian Federation.
5. Stavropol State Agrarian University, Stavropol, Russian Federation.